
Editor's Note A newly developed predictive model offers healthcare professionals a dynamic tool to assess the risk of nosocomial infections (NIs) in patients following colon cancer surgery, potentially improving early intervention strategies. Published February 27 in Frontiers in Oncology, the study introduces a nomogram—a statistical model that visualizes key risk…

Editor's Note A cohort study published February 24 in JAMA Pediatrics found that prophylactic antibiotics reduced the odds of surgical site infections (SSIs) by 72% in children undergoing cholecystectomy for uncomplicated cholelithiasis. However, extended-spectrum antibiotics offered no additional benefit over cefazolin, suggesting that simpler prophylaxis protocols could optimize outcomes while…

Editor's Note A large international clinical trial found that incisional negative pressure wound therapy (iNPWT) does not reduce surgical site infections (SSIs) following emergency laparotomy. The SUNRRISE trial, conducted across 34 hospitals in the UK and Australia and published January 27 in Jama Network, randomized 821 patients to receive either…

Editor's Note A cohort study conducted across 10 hospitals in the Mass General Brigham system found that stopping universal masking and SARS-CoV-2 testing significantly increased hospital-onset respiratory viral infections, while reinstating masking for healthcare workers reduced those rates. As detailed in a November 27 research letter in Jama Network Open,…
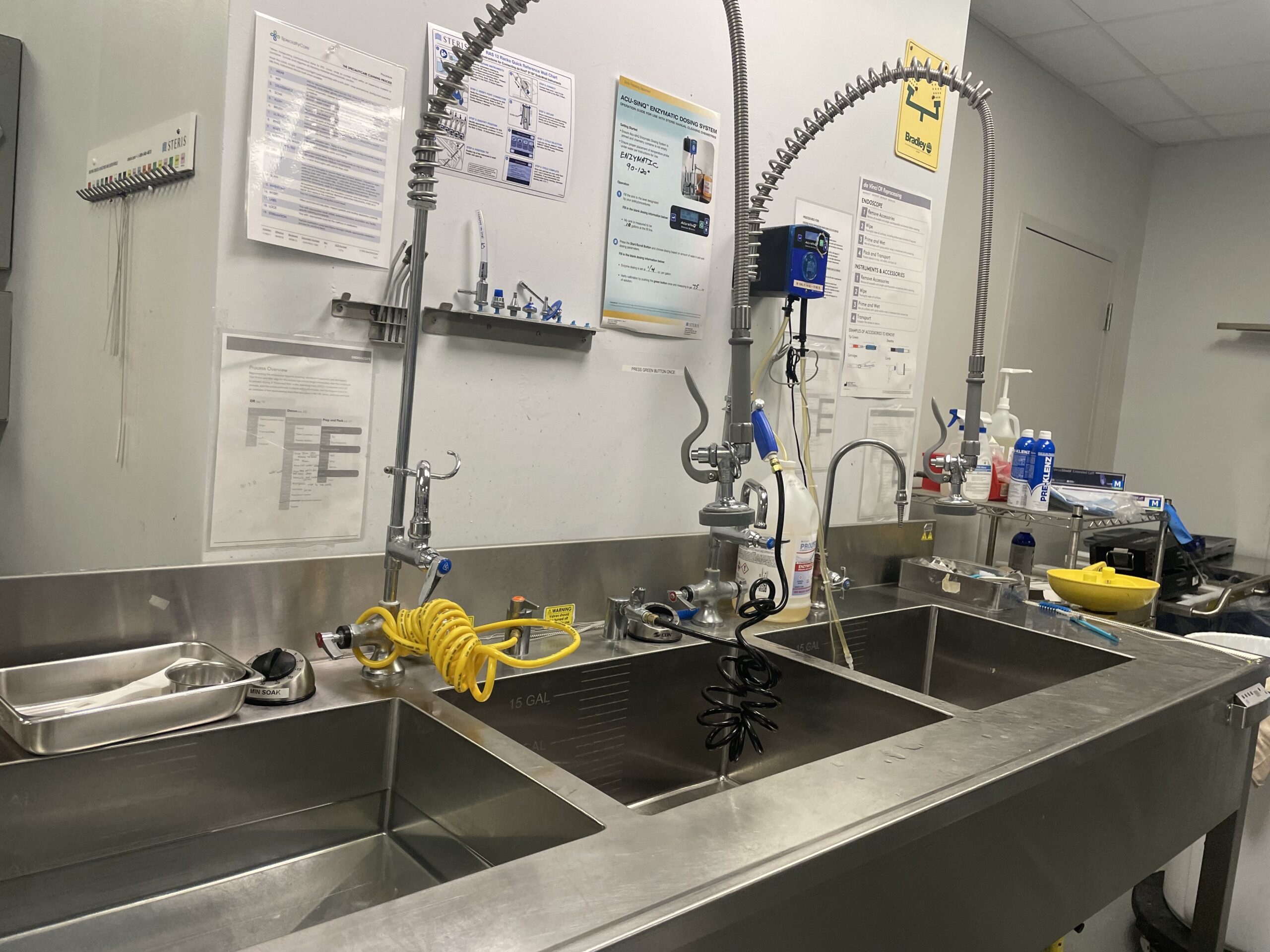

Asking who, what, why, when, where, and how—otherwise known as the “5 Ws and an H”— is a time-tested way for writers and researchers to ensure comprehensive coverage of any topic. Here, we apply this framework from the perspective of sterile processing department (SPD) professionals seeking to start a water…

Editor's Note Optimizing patient positioning can help reduce the risk of surgical site infections due to airborne contaminants in positive-pressure ORs, according to a study published August 12 in Nature: Scientific Reports. Maintaining higher pressure than adjacent spaces prevents entry of contaminants from environments external to the OR. For this…
Reforming instrument reprocessing practices does not always end with the main sterile processing department (SPD). Holding clinics to the same standard adds to the challenge, whether they are associated with hospitals or operate independently. Nonetheless, standardization is just as essential to maintaining efficiency and quality standards. Establishing and maintaining best…

Editor's Note A study published May 7 in JAMA Open found no significant risk of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) when colonoscopy is performed within one year of total joint arthroplasty (TJA), whether the colonoscopy was done before or after the surgery. However, certain comorbidities such as kidney and pulmonary disease,…
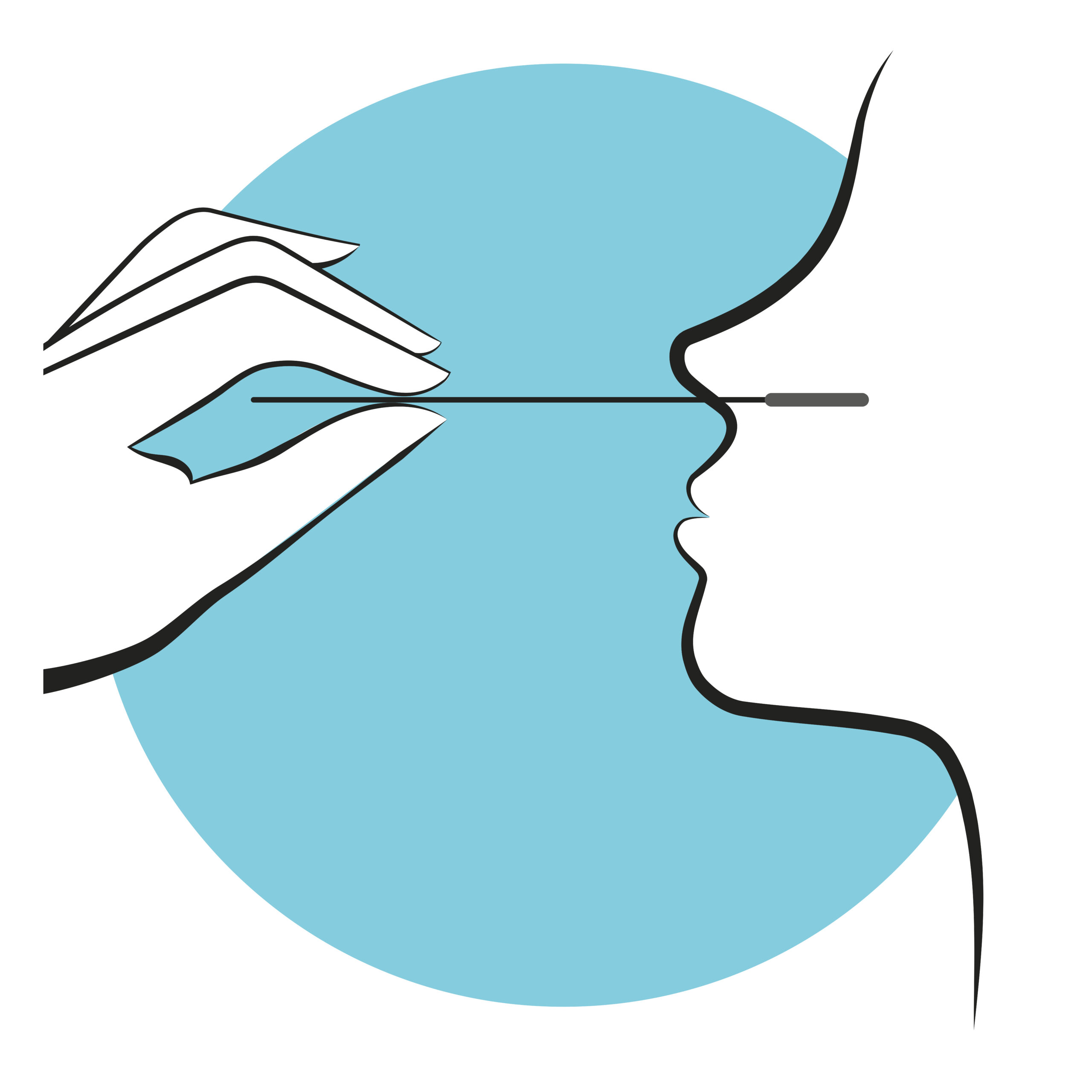
Over 20 years ago, an article from Johns Hopkins published in The New England Journal of Medicine showed that Staphylococcus aureus decolonization of the nares can decrease risk of surgical site infections (SSI). Since then, nasal decolonization—the application of a topical antimicrobial or antiseptic agent to the nares—has been adopted…

Editor's Note New World Health Organization (WHO) guidance aims to prevent the occurrence of bloodstream and other infections caused by improper use of catheters during medical procedures. Released May 9, the global guidelines focus on insertion, maintenance, and removal of catheters during medical procedures, which can damage organs and cause…